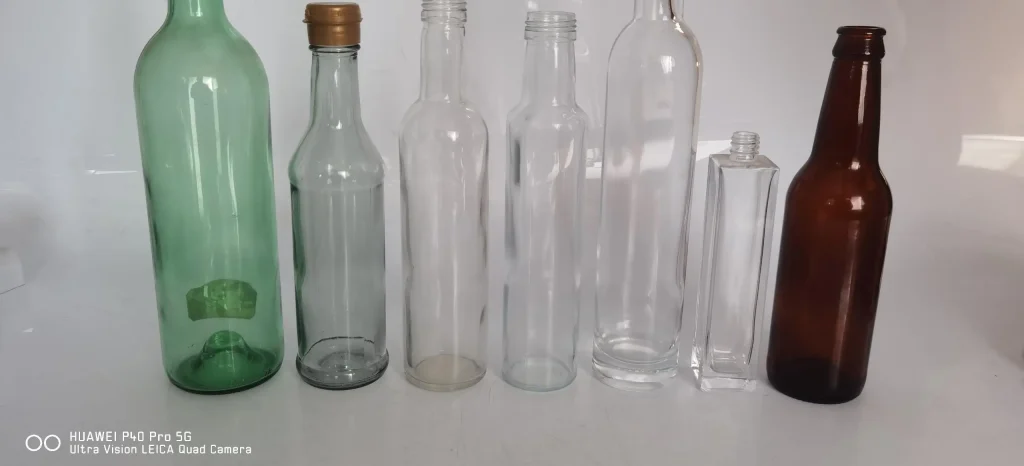
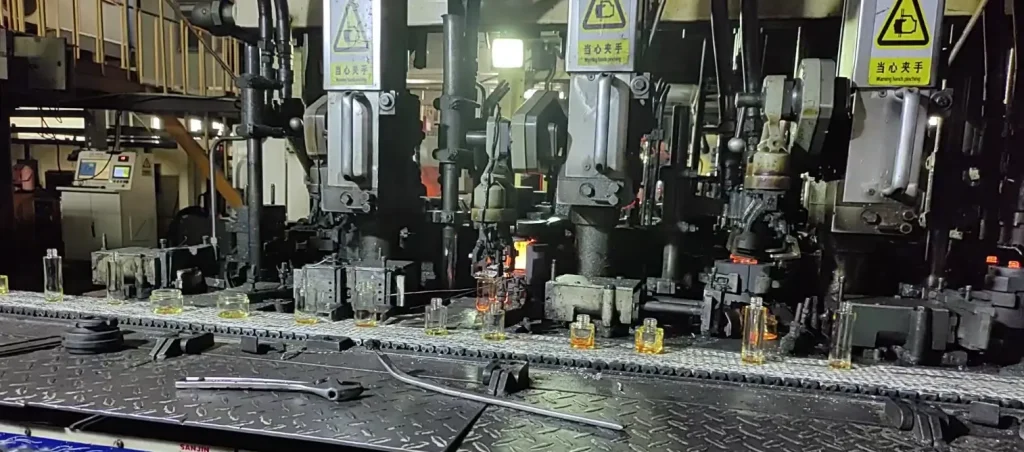
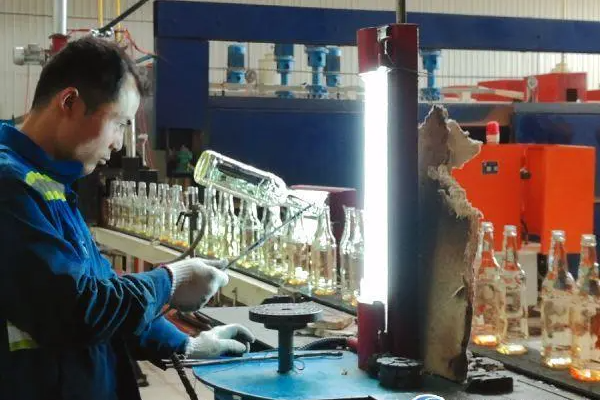
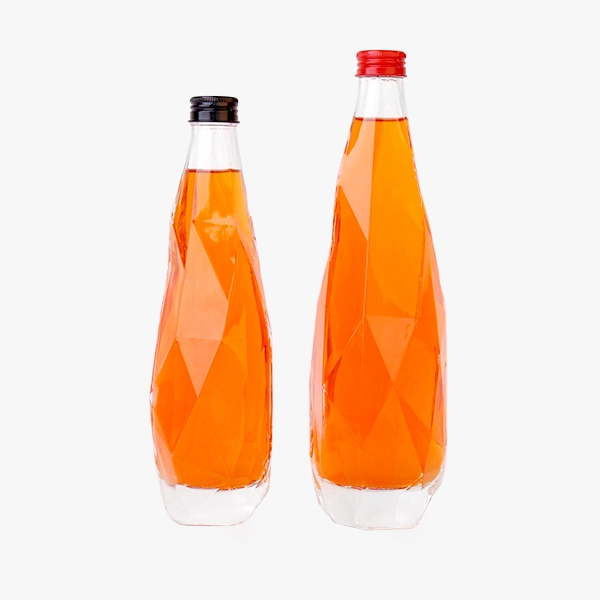
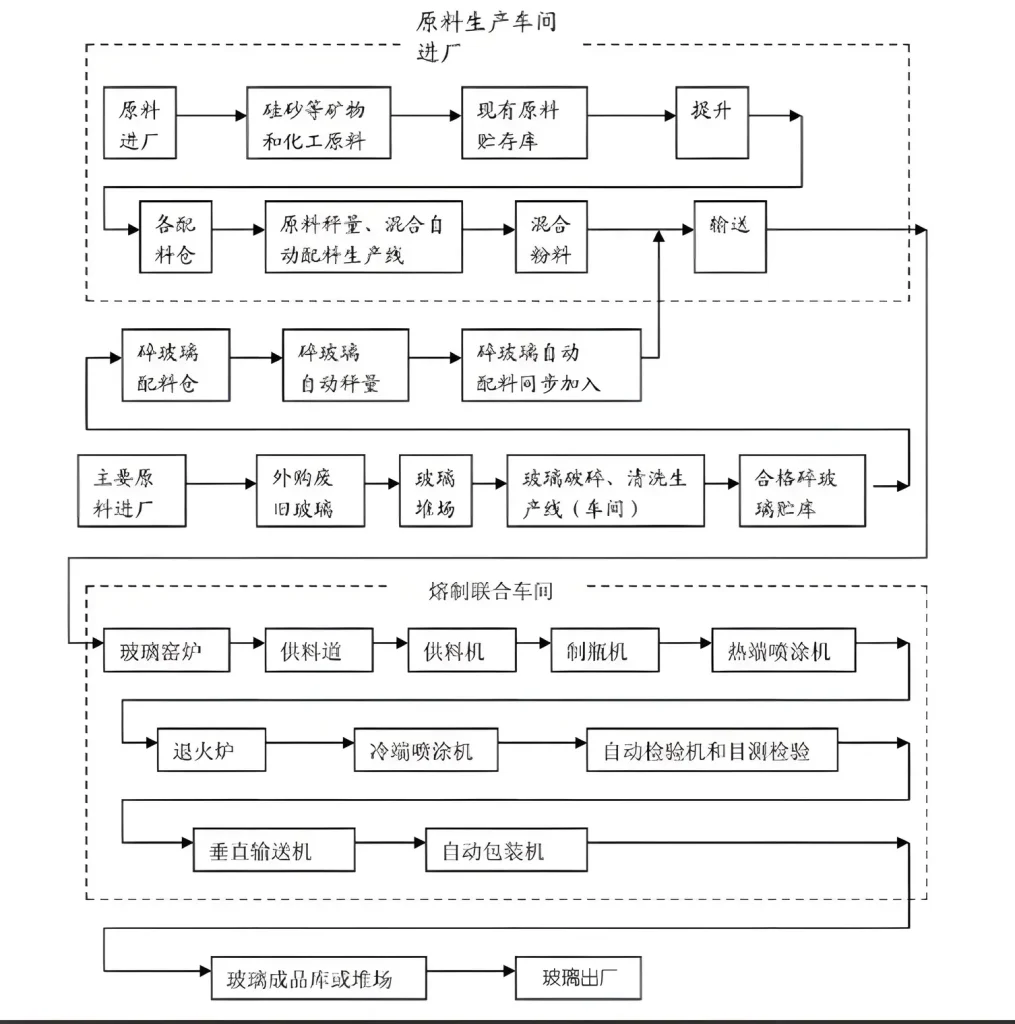
Food Packaging
Beverage Packaging
Spirits Packaging
Beer Packaging
Wine Packaging
Cannabis Packaging
Glass Mason Jar
 wholesale hot sauce bottles
wholesale hot sauce bottles
 Glass Candy Jars Wholesale
Glass Candy Jars Wholesale
 Chutney Jars
Chutney Jars
 coffee grinder
coffee grinder
 Glass Coffee Jars
Glass Coffee Jars
 Glass Honey Jar Manufacturer
Glass Honey Jar Manufacturer
 Glass Salad Dressing Bottle
Glass Salad Dressing Bottle
 Glass Spice Jar Manufacturer
Glass Spice Jar Manufacturer
 Glass Syrup Bottles Wholesale
Glass Syrup Bottles Wholesale
 Jam Jelly Jars Wholesale
Jam Jelly Jars Wholesale
 Olive Oil Bottles Wholesale
Olive Oil Bottles Wholesale
 overnight oats jar
overnight oats jar
 pickle jars wholesale
pickle jars wholesale
 Salsa Jars Wholesale
Salsa Jars Wholesale
 butter churn
butter churn
 Borosilicate Glass Jars
Borosilicate Glass Jars
 salt pepper grinder
salt pepper grinder

 wholesale hot sauce bottles
wholesale hot sauce bottles
 Glass Candy Jars Wholesale
Glass Candy Jars Wholesale
 Chutney Jars
Chutney Jars
 coffee grinder
coffee grinder
 Glass Coffee Jars
Glass Coffee Jars
 Glass Honey Jar Manufacturer
Glass Honey Jar Manufacturer
 Glass Salad Dressing Bottle
Glass Salad Dressing Bottle
 Glass Spice Jar Manufacturer
Glass Spice Jar Manufacturer
 Glass Syrup Bottles Wholesale
Glass Syrup Bottles Wholesale
 Jam Jelly Jars Wholesale
Jam Jelly Jars Wholesale
 Olive Oil Bottles Wholesale
Olive Oil Bottles Wholesale
 overnight oats jar
overnight oats jar
 pickle jars wholesale
pickle jars wholesale
 Salsa Jars Wholesale
Salsa Jars Wholesale
 butter churn
butter churn
 Borosilicate Glass Jars
Borosilicate Glass Jars
 salt pepper grinder
salt pepper grinder